Authentication Context
Overview
The Authentication Context is designed as an independent microservice responsible for user authentication, credential management, and secure session handling.
Main Entities
Account: Represents the authentication credentials of a user. Stores only the password hash, never the plain password and associates it with a user ID.
- Password Hash: Securely hashed password.
- User ID: Unique identifier for the user in the system.
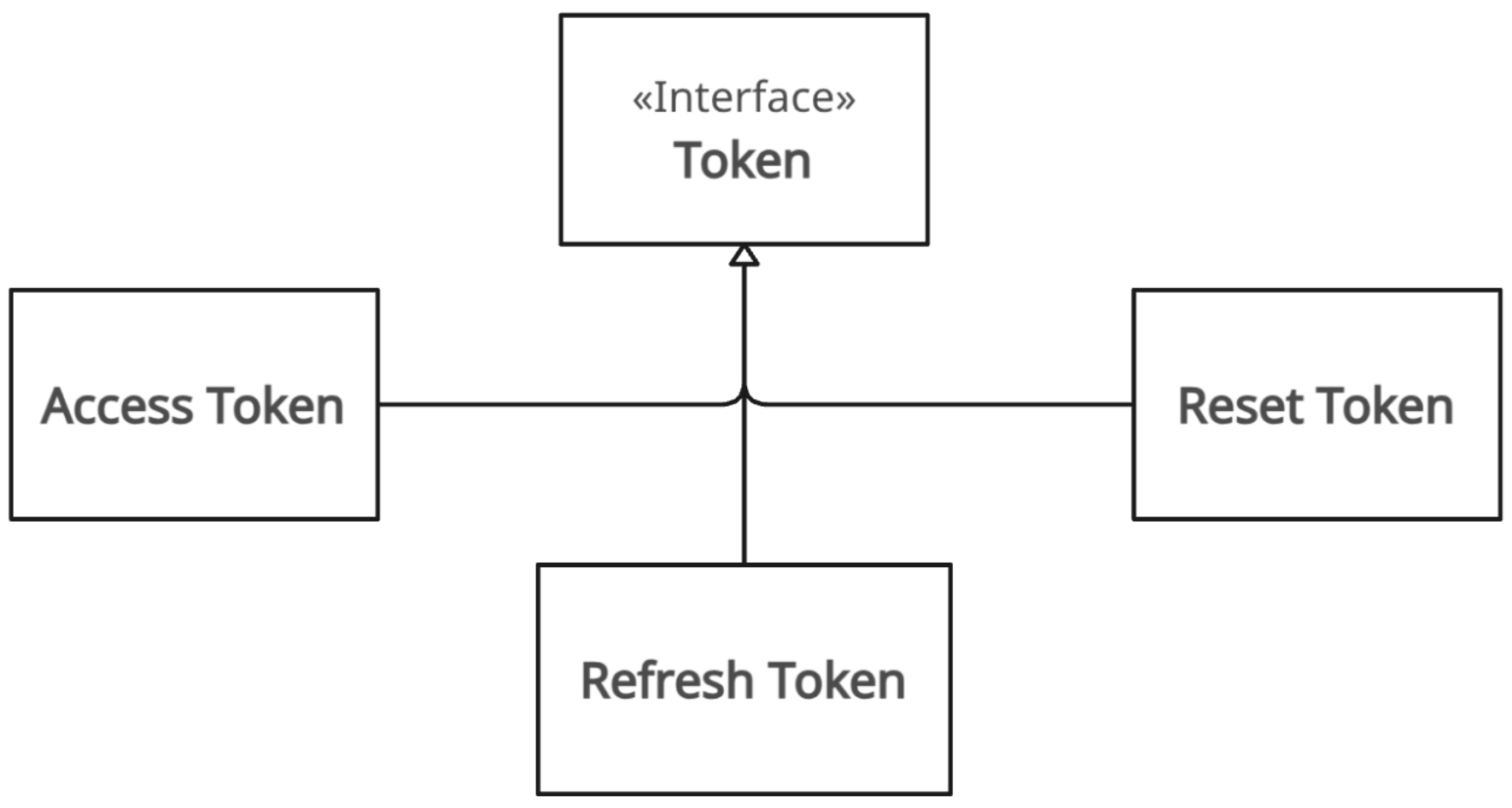
Token: Represents session and access grants. It can be:
- Access Token: Short-lived token for API authentication.
- Refresh Token: Long-lived token, stored server-side for session renewal and revocation.
- Reset Token: Single-use token for password reset flows.
User: Minimal user information required for authentication (ID). Full user profiles are managed in a separate context.
Components
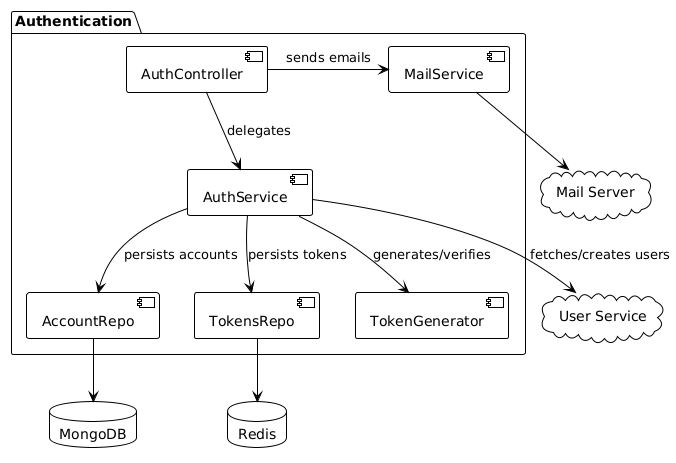
The Authentication Context is organized into the following components:
Controller: Handles HTTP requests and responses, validates input, and delegates to the service layer.
Auth Service: Encapsulates authentication logic, orchestrates operations across repositories, token management.
Repository Layer
- Account Repository: Stores and retrieves account credentials.
- Token Repository: Persists refresh and reset tokens, including blacklisting for logout or security.
Token Generator: Handles token creation, validation, and expiration for access, refresh, and reset tokens.
Mail Service: Sends registration and password reset emails using a pluggable mail client.
UML Class Diagram
Alternative Designs Considered
- Stateless Token Only Using stateless JWTs without server-side storage was considered, but rejected to enable token revocation (logout, password reset) and blacklisting.